ECOrepono Solar Project Management

Solar project management entails the meticulous oversight and coordination of every phase of a solar energy project, from the initial planning stages to final implementation. This comprehensive process includes tasks such as site analysis, feasibility studies, budgeting, procurement, scheduling, resource management, and regulatory compliance. The ultimate objective is to ensure the successful completion of solar projects, whether they are small-scale installations or expansive utility-scale solar farms.
Rooftop solar project management specifically focuses on the coordination and execution of solar installations on the rooftops of various buildings, including residential, commercial, and industrial structures.
Small-Scale Installations in Residential Areas
Solar project management for small-scale residential installations involves the careful planning, execution, and oversight of solar energy systems designed for individual homes or small residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
The process includes several key steps
Initial Consultation and Site Assessment:
- Energy Needs Assessment: Understanding the homeowner’s energy requirements and goals.
- Site Analysis: Evaluating the roof or property for solar potential, including factors like sun exposure, shading, and structural integrity.
Design and Feasibility:
- System Design: Creating a customized solar system layout that maximizes energy production and fits the aesthetic of the home.
- Feasibility Studies: Conducting financial and technical analyses to ensure the project’s viability and return on investment.
Permitting and Approvals:
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating local building codes, zoning laws, and obtaining necessary permits.
- Utility Interconnection: Coordinating with utility companies for grid connection and net metering agreements.
Procurement and Installation:
- Equipment Sourcing: Procuring high-quality solar panels, inverters, and other system components.
- Installation: Managing the physical installation of the system, including mounting panels, wiring, and connecting to the electrical system.
Testing and Commissioning:
- System Testing: Ensuring the system operates correctly and efficiently.
- Commissioning: Officially starting the system and monitoring initial performance.
Ongoing Maintenance and Support:
- Maintenance Plans: Providing routine maintenance services to ensure optimal performance.
- Customer Support: Offering ongoing support for any issues or questions the homeowner may have.
Solar Project Management for Utility-Scale Solar Farms
Solar project management for utility-scale solar farms involves the development and oversight of large-scale solar energy installations that generate significant amounts of electricity for the power grid.
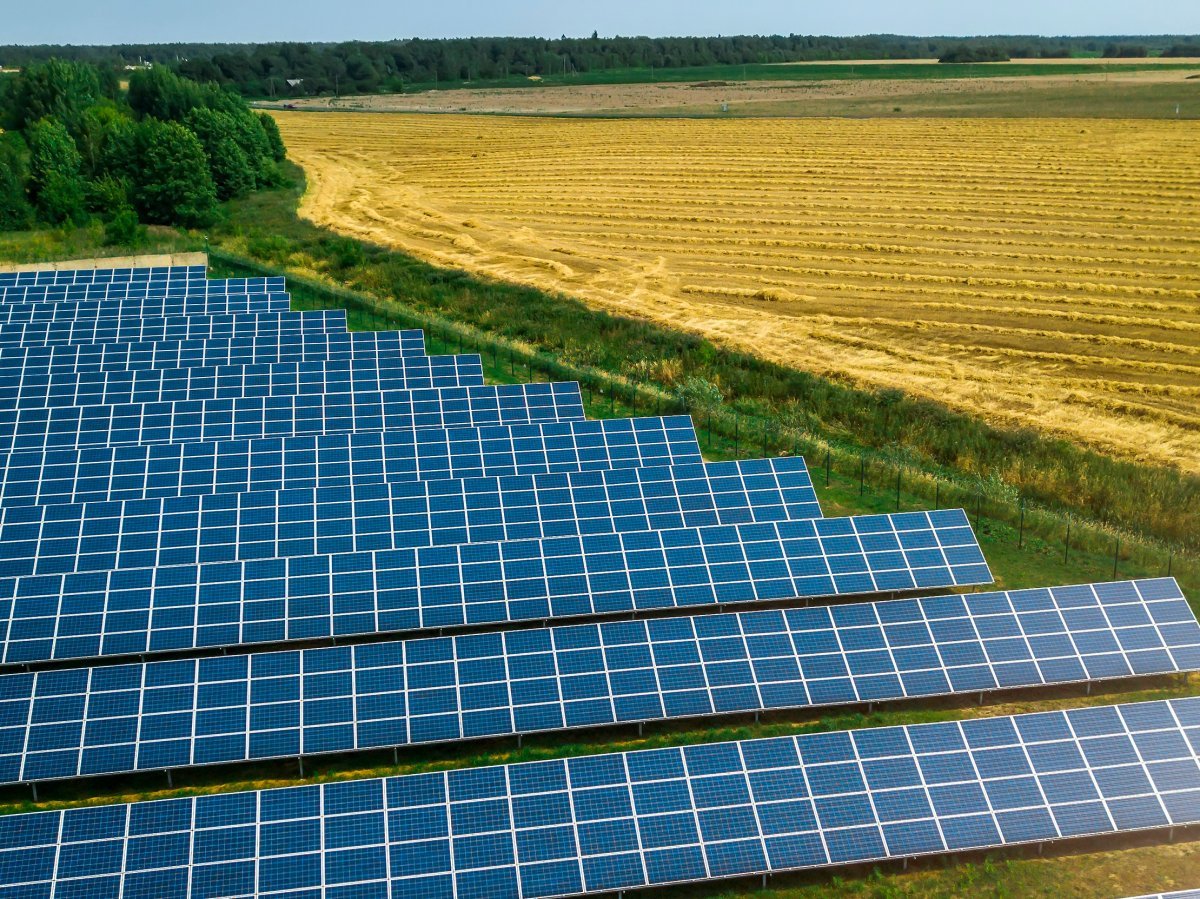

The process includes several key steps
1. Site Selection and Acquisition
- Land Acquisition: Identifying and securing large tracts of land suitable for solar farm development, often in open areas such as fields, deserts, or other undeveloped land.
- Environmental and Site Assessments: Conducting thorough environmental impact assessments and site surveys to ensure the chosen location is viable and sustainable. This includes analyzing soil quality, topography, and potential ecological impacts.
2. Design and Engineering
- System Design: Developing detailed plans for the solar array layout, electrical infrastructure, and interconnection with the power grid. This includes the positioning of solar panels, inverters, transformers, and other essential components.
- Engineering Solutions: Creating engineering plans to maximize efficiency and minimize costs, including considerations for optimal panel tilt, spacing, and orientation to capture the most sunlight.
3. Permitting and Compliance
- Regulatory Approvals: Obtaining all necessary permits and approvals from local, regional, and national authorities. This may involve navigating complex regulatory landscapes and ensuring compliance with environmental, zoning, and construction regulations.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Working with local communities, government agencies, and other stakeholders to address concerns, gain support, and ensure the project aligns with regional development plans.
4. Financing and Investment
- Securing Funding: Arranging capital investment required to finance the project. This often involves multiple investors and financial institutions, as well as securing grants, loans, or other financial incentives.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Establishing long-term agreements with utility companies or other power purchasers to sell the electricity generated by the solar farm. PPAs provide a stable and predictable revenue stream, which is crucial for securing investment.
5. Construction and Installation
- Procurement: Sourcing large quantities of high-quality solar panels, inverters, mounting systems, and other necessary equipment.
- Construction Management: Overseeing the construction process, including site preparation, installation of solar panels and electrical systems, and ensuring safety and quality standards are met.
- Installation: Managing the physical installation of the solar arrays, wiring, and connection to the grid, often involving large teams of specialized contractors.
6. Operations and Maintenance (O&M)
- Monitoring and Management: Continuously monitoring the performance of the solar farm using advanced data analytics and monitoring systems to ensure optimal operation.
- Maintenance Services: Providing regular maintenance to prevent and address any issues, including cleaning panels, checking electrical connections, and repairing or replacing faulty components.
7. Data Analytics and Reporting
- Performance Analytics: Using data analytics to track energy production, identify trends, and optimize the performance of the solar farm.
- Reporting: Providing detailed reports to investors, regulatory bodies, and other stakeholders on the system’s performance, financial status, and environmental impact.

